"A nation that does not know its past does not understand its present, and cannot create its future!"
Europe needs Hungary... which has never let itself be defeated
The Council of Trent. The beginning of the Counter-Reformation in Europe. Catholic renewal in Hungary
The Council of Trent (1545 – 156 3)
After Márton Luther's action /1517/, nearly decades had to pass before the Roman Catholic Church organized and then convened the meeting that brought about Council of Trent . (Now Trentino , a city located at the foot of the Alps Northern
Italy.) The synod is the main assembly of the church, which is attended by leading priests the pope at the head . The most important religious , disciplinary, and organizational tasks are discussed here .
Roman Catholic which had sunk into indolence and comfort for a millennium and a half, was shaken by the reformation coming from outside. It was Rome's "luck" that the views of Luther and Calvin were radically different from each other , and even contradicted each other on many points. Luther even professed that "I myself am the explanation of my doctrines!" However, Calvin went further when he taught that the church should penetrate deeply into every part of private and public life.
The reforming Protestant churches set an example for Rome to realize that there are many unnecessary elements in the liturgy. Renewal can only be achieved if several practices that were often incomprehensible to ordinary people are left out of the service.
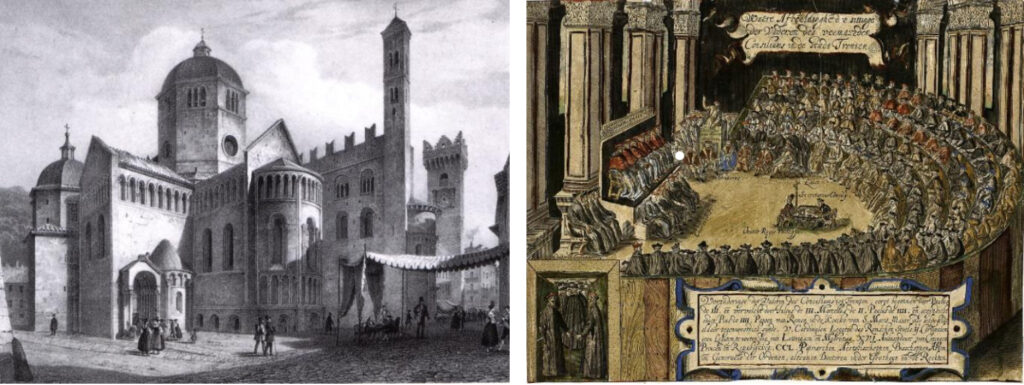
The site of the Council of Trent, the San Cataldo Cathedral in the 19th century. The meeting hall of the synod with the 255 conferring high priests. (Matthias Burglechner)
When we talk about the rapid spread of the Reformation, the image that remains in most people's minds is that the whole of Europe was conquered by the Protestant religion to a similar extent. However, the reality was that Catholic survival encompassed much larger areas and masses than we would imagine after the Protestant conquest. The population of Europe in the 16th century can be estimated at around 95 million. Of this, Spain and Portugal, encompassing an entire world empire, had 10 million inhabitants. The other Mediterranean state, Italy, with its 13 million Catholic population, was the most densely populated region in Europe. The most populous city in Europe in the 16th and 17th centuries. century, it was Naples with a population of three hundred thousand. France, which also remained Catholic, has a population of 16 million. The German Empire of 20 million was divided. Most of the northern parts converted to the Protestant faith, in southern German Bavaria, after minor wars, the Catholic religion remained. (Data from Konrád Szántó)
The initial successes of the Reformation filled the Protestant believers and their leaders with great hope. In the 1570s, they ruled many countries with a ratio of around 40%. By the middle of the 17th century, thanks to the successful policy of the Counter-Reformation, this proportion dropped below 25% in Europe. The struggle between religion and religion was changed by two devastating events. One of them was the great plague, which took its toll mostly in the countries of the Mediterranean Sea - Spain and Italy. However, this biological disaster did not only affect the region dominated by Roman Catholics, but also the Reformed regions. As a result of the war, it spread to the countries of the German-Roman Empire. The other devastating event was the Thirty Years' War (1618-1648) raging on German soil, which was also called "Europe's First World War" due to the loss of nearly 13 million people. Rightly so, since Germany's population of twenty million fell to seven million. (Pierre Chaunu's data) The two devastating events are related, because where dense masses of people move - this is the military - it is inevitable that the plague will be brought into the barracks. In Hungary, during the castle wars that began in 1552 - for example at the siege of Eger - the Turkish army was also decimated by the plague, which the retreating Turkish army then dragged into Constantinople with them.
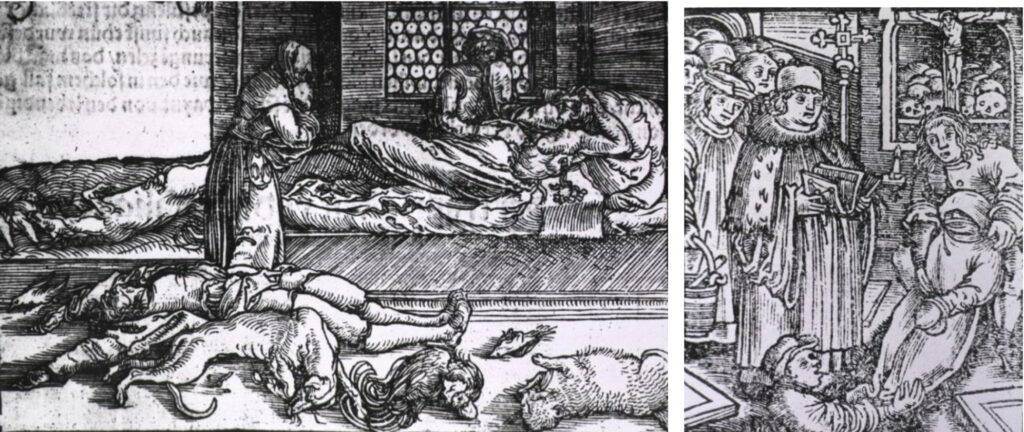
Woodcut illustrating the devastation of the plague. Burial of those who died in the plague (semmelweismuzeum.blog.hu)
The Catholic Renewal
, which lasted for 18 years by sharp debates, the death of four popes and breaks , was by IV. It was closed by Pope Pius. The main points really brought about a change compared to the time of Leo X. The first is that a catechism that included Catholic teaching and moral principles. Priest training played a prominent role . Great importance was placed religious education in the church . Furthermore , high priests could only hold one dignity they had to deal with the affairs of . A list of prohibited books was compiled , "heretical" books were added to the index. They advocated the setting up of printing presses , seeing role of books and reading the Protestants . veneration of saints, relics, and holy images prominent role , above all the veneration of Mary . The farewell cards .
The " first " Catholic Bible - translations were born on the Protestant model . (The Vulgate is the Latin translation of the Bible, which was developed in the 5th century . The 16th century Catholic Bibles are actually not new creations, but the more than a thousand-year-old Vetus Latina into the new Catholic The Inquisition , which is the most severe punishment reported, was given to the authority of the Pope .
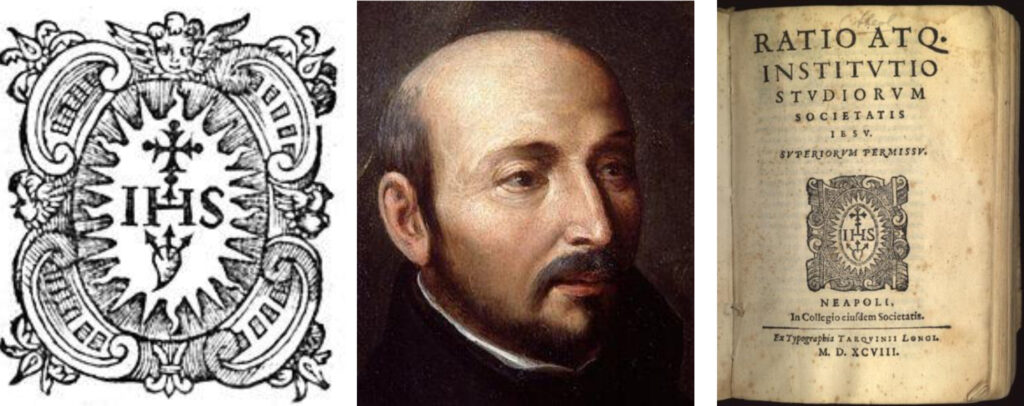

Coat of arms of the Society of Jesus (1586) St. Ignatius of Loyola, founder of the order Title page of the Ratio atque institutio studiorum Societatis Iesu, the study regulations of Jesuit schools introduced in 1599 and valid for a long time
The high priests knew that it would be useless to make decrees and formulate nice - sounding points for the sake of renewal, if there were no orders , no people could implement the Trident decisions . It
created for this task already in 1540 by III. Pope Paul the Jesuit order . The task of the order of the Jesuits, i.e. the Society of Jesus was not only to push back the Reformation spread the Catholic religion throughout the world - primarily in the Spanish and Portuguese colonies Speaking of the Jesuits, we cannot avoid the life of Ignatius of Loyola , which is important for our topic. The nobleman of Basque (non-Spanish) origin the military and practiced the science of weaponry with great pleasure. many bloody battles, learned the secrets of love, and was among the first in warfare. On Pentecost 1521, a French cannon ball hit his leg, which radically changed the life of the hitherto vain soldier. his recovery a heavenly miracle , and from then on he no longer served the King of Spain, but Jesus, the lord of heaven and earth. If the legend is to be believed, during the long hospitalization he only got two books, that's all. One the Life of Jesus , the other Life of the Saints .
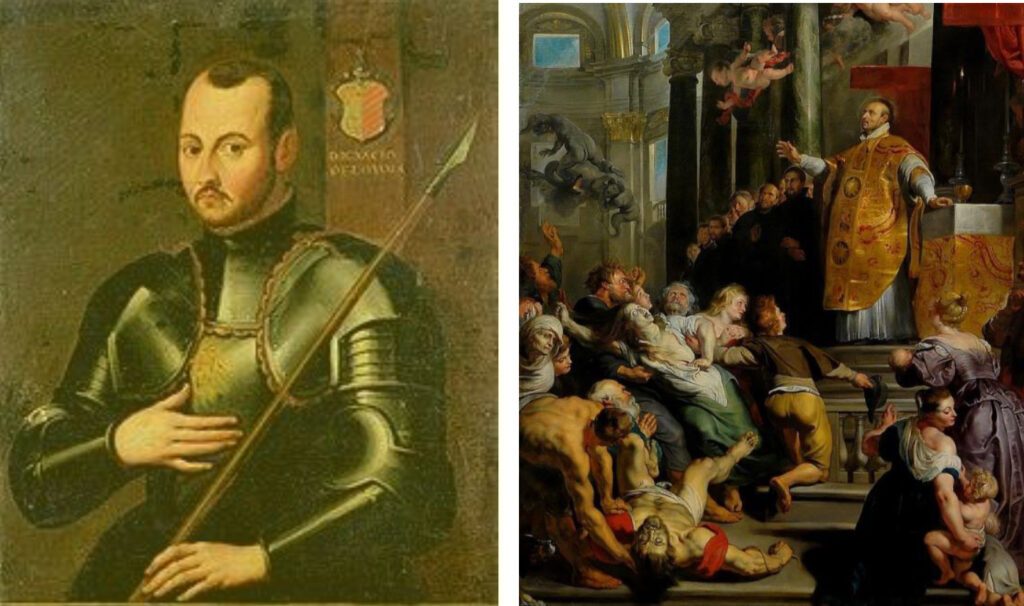

Ignatius of Loyola as a young man in military armor. The military nature of the Jesuit order can perhaps be connected with the life of the young military officer. The leader of the Jesuit order was the general among the followers of St. Ignatius of Loyola (work by Peter Paul Rubens)
After leaving the hospital, had to travel a long way - both in space and time - until he felt that he was prepared to serve the Lord. the Manréza monastery, he wrote the work
Lelkigyakorlatok was the beginning of his pathfinding. He went on a pilgrimage to the Holy Land as a beggar, and after returning from there he visited Rome, Barcelona, Salamanca, and Paris. studying and preaching, the church authorities noticed him, suspicious , and the Inquisition even imprisoned Ignatius They couldn't decide whether he was a subversive heretic or a well-intentioned reformer? He was released, so he could continue his activities . In Paris in 1534 , they made an alliance with some true believers , including St. Xavier and Péter Fáber, path of poverty and the service of the cross . The Society of Jesus was founded here in 1540 , which was approved by the Pope. The number of members of the order increased rapidly, and soon spread throughout Europe , and the Jesuits even areas of (India, the Far East ) . When Ignatius of Loyola died on July 31 , , the Council of Trent was still in full swing. Maybe he didn't even think about what a great organization he left behind. After all, under the influence of the Jesuit order society of the Oratorians the order of the Merciful the Capuchins , the Lazarists , the women's order of the Anglican nuns , or the Piarists who were set up

The tomb of Ignatius Loyola is located in the Il Gesu church in Rome. Il Gesu is the first baroque church in Europe. Baroque, as an architectural style and cultural concept, was almost completely intertwined with the Counter-Reformation. Saint Bartholomew's Night in Paris
János Kálvin spread in France as well. the French Reformed, the Huguenots and the Catholics ended in a bloody event. On the night of
August 23 , (St. Bartholomew's Day), the lodgings of the French Huguenot leaders who had gathered in Paris for a conference were and massacred by the Catholics In the ensuing battles, around twenty thousand Huguenots lost their lives, but with this France remained on the Roman Catholic faith.
The famous saying of the Protestant French King Henrik Bourbon is connected to this event : " Paris is worth a mass." That is, the king converted to the Catholic faith, so he could keep his power.
Counter-Reformation in Hungary
The reformation in Hungary – as already mentioned in the previous chapter – differently than in the western half of the continent. of
the country into three parts , the creation of the "reformed" Principality of Transylvania, and the absence of a religious war similar to bloody German , English , There were conflicts in Hungary as well, which often claimed human lives, or ended only in the fact that the Catholic church one or another settlement was occupied by the Reformed . the frescoes, took out the statues and pictures of the saints replaced the altar, The result of this can visit
intact Árpád - era churches , which under management of the Reformed Church . Let's think of Vizsoly, Ócsá, Nyíracsád, Karcsá, Tákos, Csaroda, as well as the dozens of churches in Transylvania, the highlands, the Subcarpathians, and the southern regions. (This should be noted because the Reformation did not yet exist in the Árpád era .)

Tákos' church on Tiszahát. In the eastern part of the country, for example in Szabolcs-Szatmár-Bereg county, the majority of the population still lives in the Reformed faith. South of Budapest, in the middle of the country, lies Ócsa, whose Romanesque-style, two-towered basilica, built in the 13th century, now serves the Reformed believers. Balatonalmádi-Vörösberény the Reformed fortress church, which changed hands several times during the Catholic-Reformed church takeovers. The Árpád-era House of God, built in the 12th and 13th centuries, is one of the rarer Reformed churches in Transdanubia.
These church occupations had many . One is the repossession of building , or in the worst case, its demolition . The other is that the faithful who were left without a new building . two or even three church buildings even in smaller . These are Roman Catholic, Lutheran (Evangelical) , Reformed, Greek Catholic, Unitarian in Transylvania, and in many you can see the building of the synagogue and the Serbian Orthodox church

Even in the smaller villages, the churches of different denominations fit well next to each other (for example, the Lutheran and the Reformed churches in Sajókaz, the Lutheran and the Catholic churches in Kővágóörs).
By the end of the 1500s, most of the country's population practiced the Protestant faith As a result of the Council of Trent, the Hungarian Catholic clergy often initiated violent . The first initiator Archbishop Miklós Oláh , who in 1561 called the current Hungarian high priests to a synod and also invited the priests of the Jesuit order to the country. The Catholic Church found a strong supporter Rudolf Habsburg , who
ascended the throne in 1576 In the country that was divided into three parts, the first attack was launched in the Highlands belonging to royal Hungary with the support of Vienna , they continued a methodical and regular persecution of Protestants.
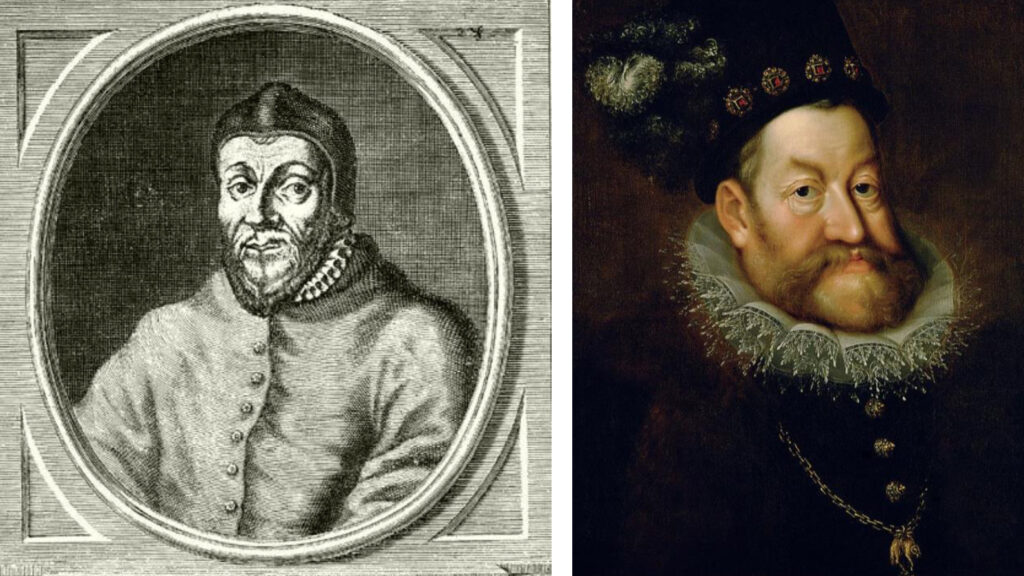

Portrait of Miklós Oláh (1493-1568). The former bishop of Eger occupied the archbishopric of Esztergom from 1553. Rudolf Habsburg (1576-1612), German-Roman emperor, who was king of Hungary between 1576-1608
The leader of the counter-reformation in Hungary at this time was Archbishop Péter Pázmány , blessed with great education, strong religious commitment, outstanding oratorical and fine writing talent . It was not an easy task
to restore the Roman Catholic faith in the country that was divided into three parts, given that three radically different religions prevail in . the Principality of Transylvania of Luther, Calvin and the Unitarians dominated the creed of the peoples living there
. In the Subjugation, the religion of Allah and the Prophet Muhammad prevailed. royal Hungary, the faith of the Roman Catholics partially remained among the majority of the people.

The main work of Archbishop Péter Pázmány Péter Pázmány of Esztergom is The Guide to Divine Justice. On its title page, we first encounter the pictorial formulation of St. Stephen's thought: Mary as patroness of Hungary
The who was born in Nagyvárad in 1570 and in Bratislava in 1637 and was buried there, described a wide-ranging career in the shaping
Hungarian history, and we can safely say, Hungarian literary history Because it is a great path when the child of Protestant parents the Hungarian Catholic faith. of his mother changed the life of the young man raised in the Protestant spirit. Miklós Pázmány of Bihar, Borbála Toldy,
instilled Catholic teachings in the young man. Avoiding Várad and birthplace , he continues his in Cluj-Napoca , but here already the Jesuit high school. After the death in 1586 of Prince István Báthory and
King of Poland , the Jesuits had to leave. The then seventeen-year-old Pázmány, together with some of his peers, was given the opportunity to continue his famous universities in Europe . In 1588 , already
lived in the Jesuit college in Krakow as a novice ( the novice period is when a monk candidate can decide whether to commit himself permanently to the service of God or to choose another path) longer a question for him that the
Jesuit a member of the order . From Kraków, he went to the Faculty of Humanities in Vienna , where he got to know many branches of Baroque education. , full of travels and studies led him to Rome , where he deepened his knowledge in the science of theology .
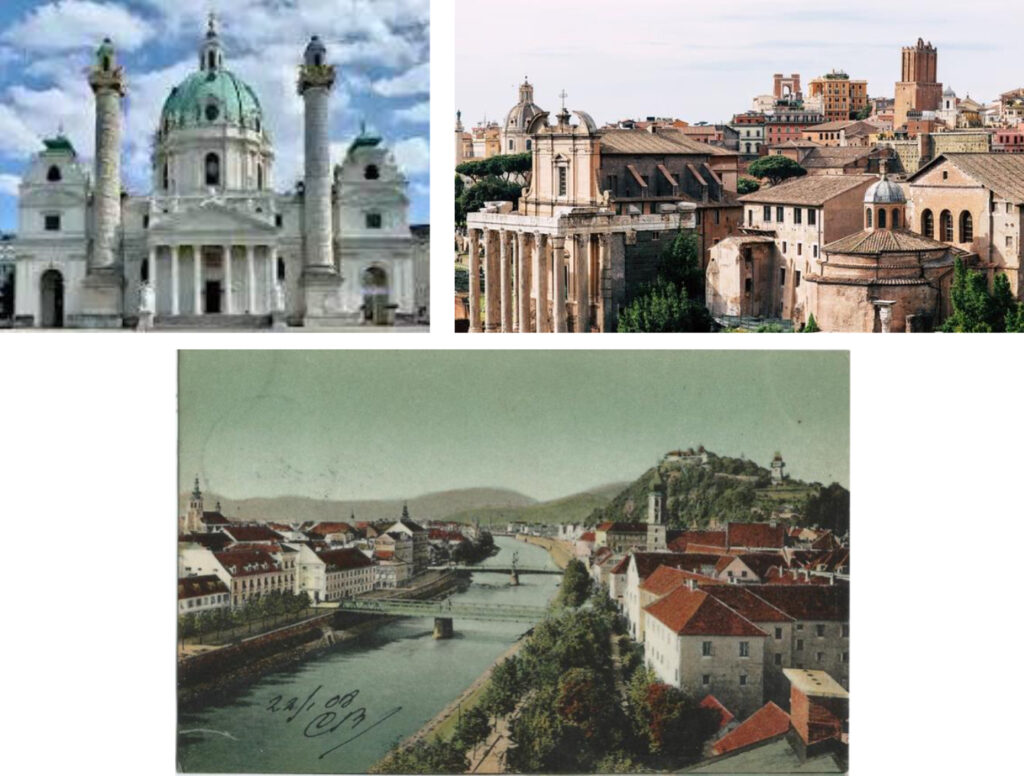

After Péter Pázmány's student years in Vienna and Rome, from 1598 he became a lecturer at the University of Graz and the supervisor of the Graz educational institution. The Baroque Károly Church in Vienna, the 15th-16th century in Rome. 19th century cityscape, the Catholic quarter in Graz can be seen in the pictures
completing his studies abroad , the leaders of the Jesuit order sent already thirty years old , to Hungary to begin his reformation activities. Péter Pázmány
began his active reformation activities the years he spent in Selly monastery 1601 to In the meantime , the southern part of the country and their surroundings in the Highlands . He visited the western and eastern parts royal Hungary as a preacher . In Kassa and its surroundings , as well as in Nitra and its surroundings , he converted to the Roman Catholic faith with speeches elegant Hungarian and . However , his highly successful speeches noticed by the country's top dignitaries . Among them were Count Miklós Forgách, Grand Master, Palatine Miklós Esterházy and several members of the Thurzó family . The nobles returned to the Catholic faith, and with them serfs, commoners, and a significant part of the population of cities. religious convictions elementary interests also played a big in the change of religion .
Let's not forget that in these years and decades there were religious disputes, new Protestant religions , church seizures, Transylvania two great powers, the plague, the Turkish invasion, and the excessive taxation of the peasants . When Péter Pázmány began his operations in Hungary, the Hajd Uprising led by István Bocskai began and the Habsburgs strengthened Vienna and the re-Catholicized Hungarian lords have a goal with the
talented Péter Pázmány, because they saw in him the man who is capable the country-wide reformation. After his first activity in Hungary returned to Graz, where he was professor of theology at the university until 1607 .
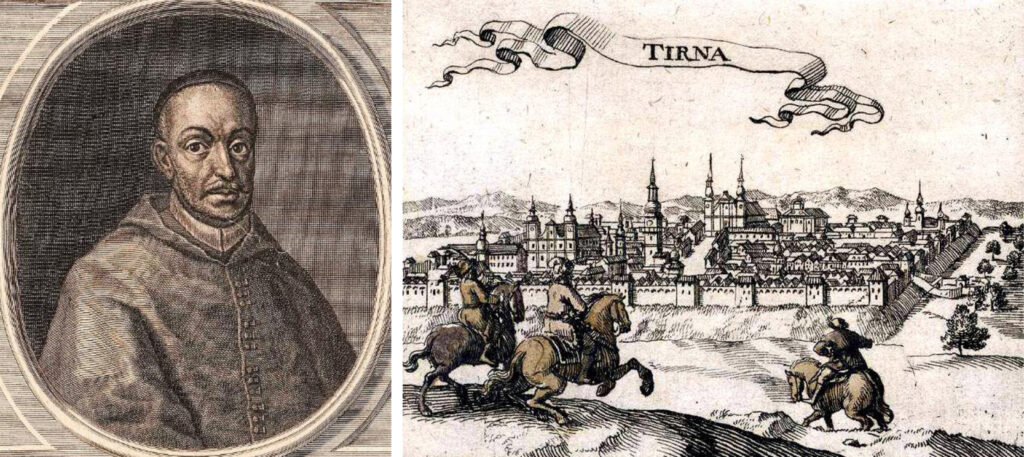

Ferenc Forgách, Archbishop of Esztergom (1566-1615), Cardinal. Copper engraving by Jeremias Gottlob Rugendas in the 18th century is a view of Nagyszombat (Tirna) in the early 1600s. The first baroque church was built in Nagyszombat, the foundation stone of which was laid in 1629 by the then archbishop Péter Pázmány. The city of Esztergom fell into Turkish hands in 1543, and until its final liberation in 1683, Nagyszombat was the archbishop's center
After his years in Graz, Pázmány was sent to Hungary for the second time, and was taken in by Archbishop Ferenc Forgách at court in Nagyszombat. Although the seat of the archbishop functioned in the town in the highlands nearly a century and a half
, the title of the country's first high priest has always remained the title of Archbishop of Esztergom. This expressed the Hungarians' belief that sooner or later Esztergom return to the bosom of the Kingdom of Hungary.
The Bratislava Parliament of 1608
the Parliament of 1608 can be felt by knowing that it defined the relationship between Hungary and the Habsburgs for a century and put it on a new foundation . Its historical and political essence was that from then on, the Habsburg
emperor, who was also the Hungarian king in one person, could not decide on the fate of Hungary in anything without the consent of the Hungarian nobility. This fact (power, national positions, property relations) returned most of the nobles
bosom of the Catholic Church. (A part of the nobility, however, still remained in the Protestant faith.) Péter Pázmány also spoke at the parliament , who in his grand speech demanded the return of the right to acquire property previously taken from the Jesuits
. Furthermore, he managed to hold a synod in Great Saturday in 1611 , which aimed to educate the clergy so that they could participate more actively in the work of Catholic reformation.
In addition to its historical importance, the 1608 Parliament also marked the beginning of the Hungarian Counter-Reformation . (It should be noted! Papal permission was needed to release Pázmány from his vow as a Jesuit monk in order to become Archbishop of Esztergom. During these years, a Jesuit could neither be
a bishop, nor a pope, nor any kind of ecclesiastical dignity.
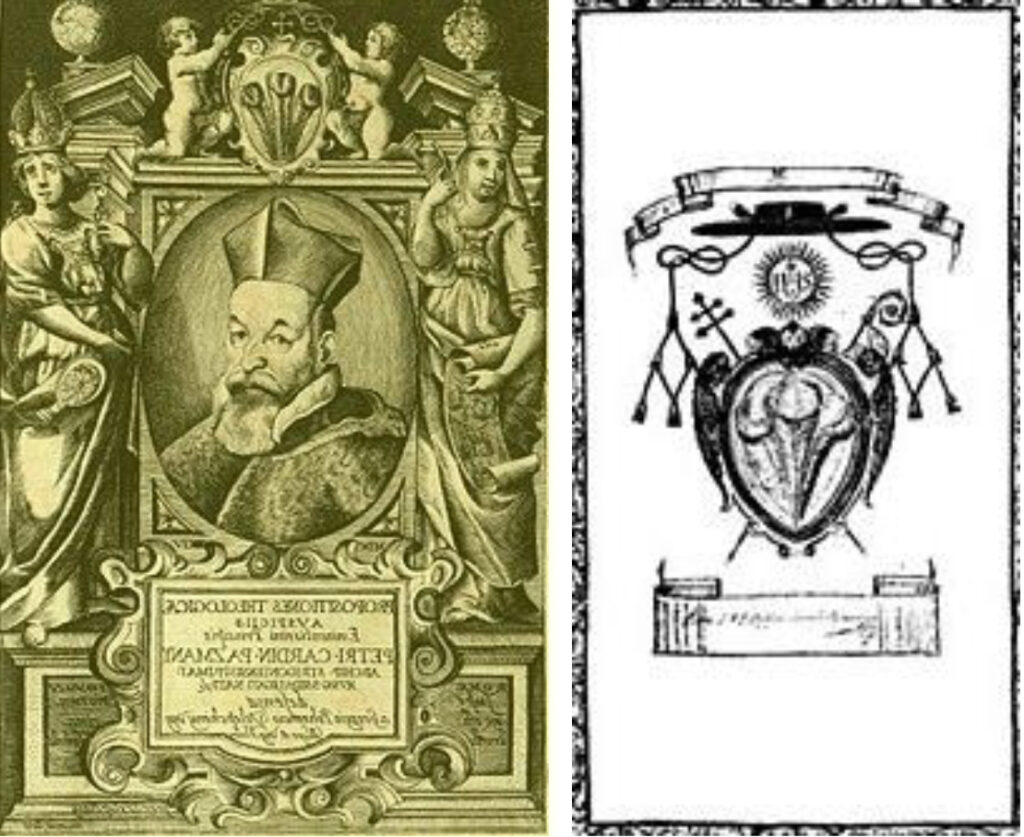
Péter Pázmány, Archbishop of Esztergom (1616-1637). Coat of arms and signature of Archbishop Pázmány
The Archbishop Jesuit Cathedral in Nagyszombat, the first church built in the Baroque style in Hungary The Catholic revival and the spread of Baroque architecture in Hungary
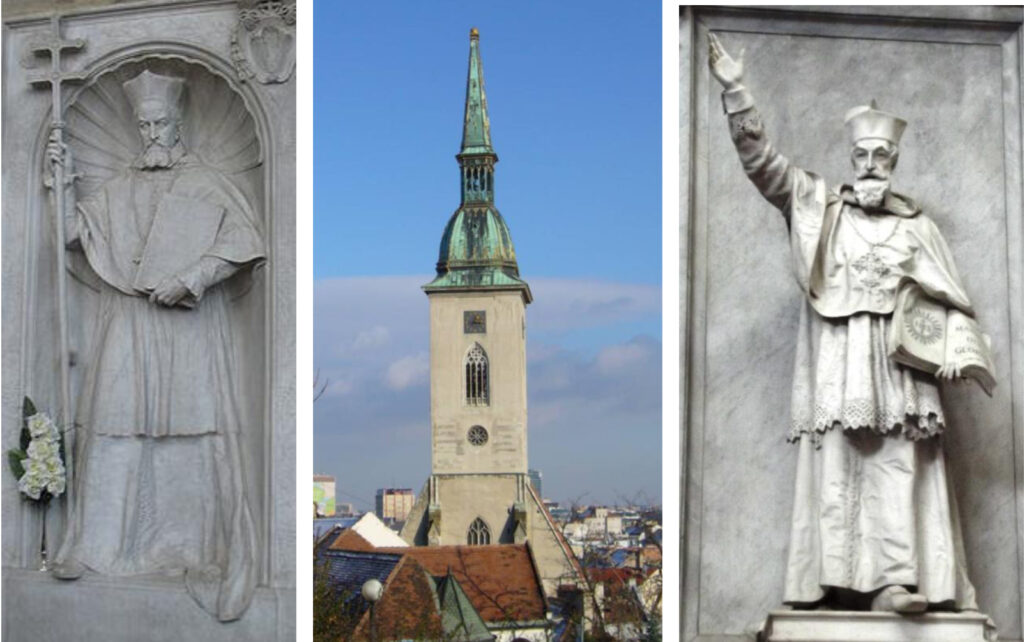

The statue of Péter Pázmány in the St. Martin's Cathedral in Bratislava. In 2010, the Slovak Bishops' Conference announced that Péter Pázmány's grave had been found in Bratislava, under the sanctuary of St. Martin's Cathedral. The coronation church in Bratislava, where the Habsburg emperors were crowned as Hungarian kings for four centuries.
It should be emphasized that the Hungarian archbishop and cardinal was almost unique among European high priests in that he converted with the weapon of fine words and persuasion and not with physical violence.
Of course, it was inevitable that as the archbishop of Esztergom, he considered all means permissible in order to suppress Protestantism, but Pázmány considered the power of words and persuasion to be the most important.
The fact that he established an educational institution for the youth in Nagyszombat in 1619 for the training of educated, moral clergy is a clear proof of his activity, and then in 1623 he established a similar school in Vienna.
The latter institute still operates today, which is known as the Pázmáneum. (The Viennese institute was rebuilt by Count Miklós Széchényi, bishop of Nagyvárad. The construction of the new Pázmány institute began in 1899.) One of the most lasting works of the great reformer is the university established in Nagyszombat in 1635, the legal successor of which is the Eötvös Loránd University of Budapest
.
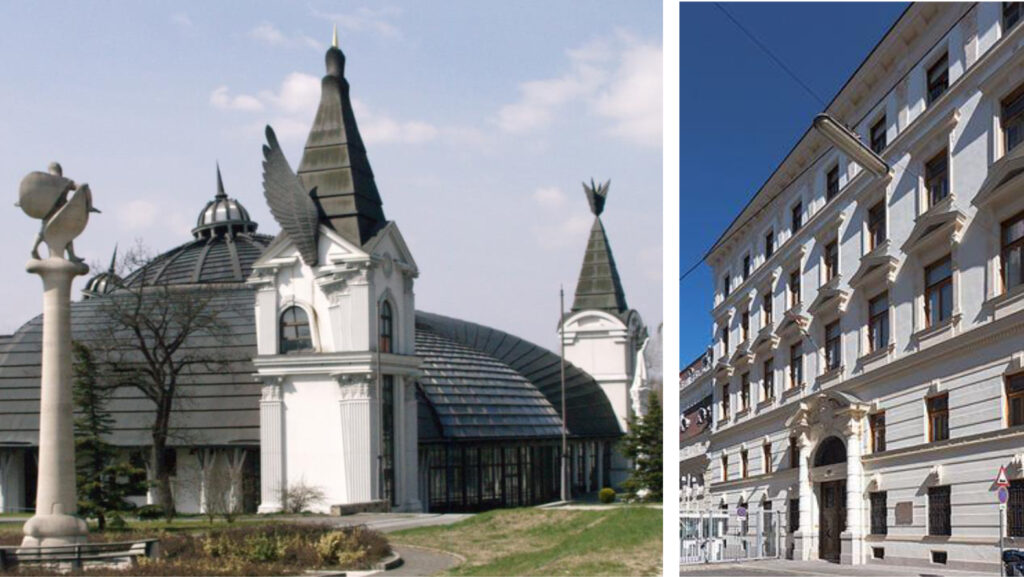

Pázmáneum buildings designed by Imre Makovecz in Piliscsaba The renovated Pázmáneum building in Vienna
(Today's Pázmány Péter Catholic University started its operation in 1993 the legal predecessor of which was the Faculty of Religious Studies of the Nagyszombat University founded in 1635. that today's Károli Gáspár Reformed University was also
- in 1993 , continuing the existing since 1855 its legal predecessor, the B udapest .)
Pázmány , as mentioned earlier , stood out among his contemporaries not only impressive speeches, but also with his unparalleled transfer of science and theological knowledge In addition to his eloquence, also excelled in his art of writing. We can rightly claim that the Hungarian literary prose . Writers and poets of later ages learned the beautiful Hungarian language from the writings of Péter Pázmány, such as Mihály Babits, Dezső Kosztolányi and many of their contemporaries.
Péter Pázmány's work as a fiction writer was impressive not only in quality, but also in quantity. The archbishop's works when the 19-20. It was published at the turn of the century, in seven thick volumes. In total, the length of the seven volumes can be estimated at nearly five thousand pages. In addition, six volumes of writings in Latin and two volumes of correspondence were published.

The title page of some of Péter Pázmány's dozens of works
the Counter-Reformation education, culture, and the sciences, which was completed in style name and concept the Baroque, the Reformation and Pázmány are inseparable from each other. the 16th and 17th centuries not only in sermons and books, but also in music, sculpture, painting, and architecture. the churches, they began to build castles in the Baroque style, several of which can still be admired today. the noble buildings seen in Fertőd, Kismarton , Keszthely, Edelény, Tata, Pápa, Sümeg some our cities also bear the Baroque style. For example, in Buda, Eger, Győr, Veszprém, Sopron.
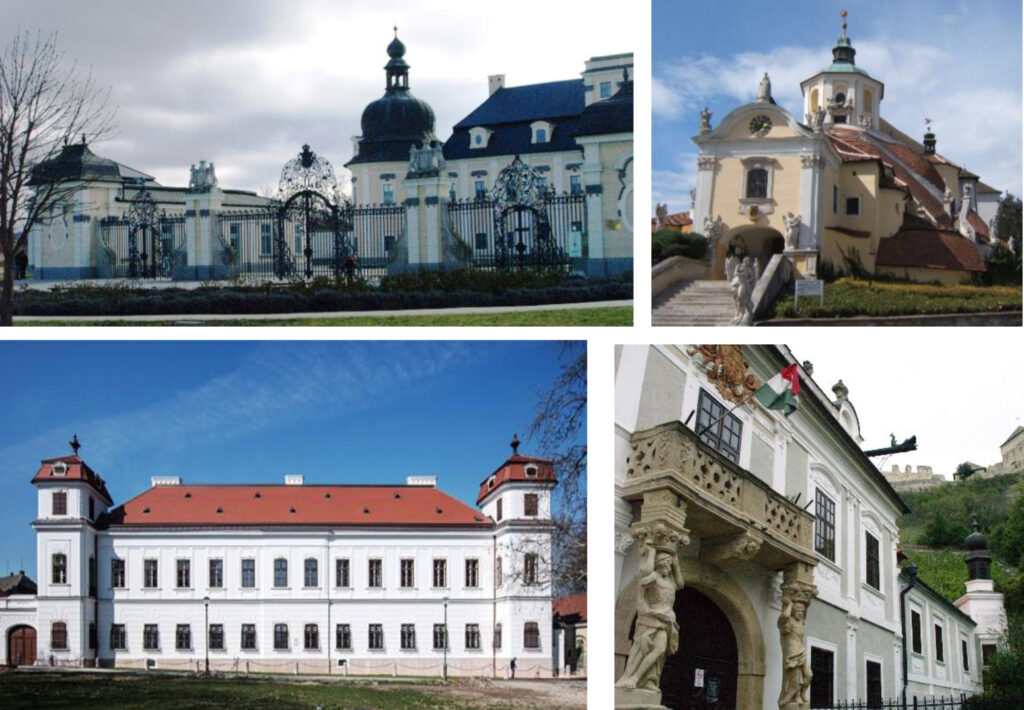

Some of the most beautiful baroque castles. Péter Pázmány also influenced architecture, as he knew that spectacular, ornate churches and castles can be attractive to ordinary people as well. Beautifully renovated baroque buildings in Edelény, Kismarton, Tata and Sümeg
the z counter-reformation also knew well that the reparations and reimbursements had to start with the noble families. , he won
about thirty high-ranking Hungarian families Among other things, he returned the great prince of Transylvania's golden age , the biblical guardian György I. Rákóczi, if not his brother, Pál Rákóczi to the Catholic ranks. no small task when he succeeded in winning Catherine of Brandenburg
who came from Protestant similar successes among the Pállfyaks, Erdődys, Draskovichs, and Hallers.
The Principality of Transylvania and royal Hungary
More and more often, I hear the summary judgment from the highest academic level to our history- interested but well-informed compatriots: the Principality of Transylvania was a Turkish mercenary, the whole, as it worked,
was the period of traitors. I note that this is not only a question of religious affiliation, but the construction of the nation after Mohács .
I will state right away that I do not agree with this point of view. Because if we accept this, then István Bocskai, Gábor Bethlen, György I. Rákóczi and Zsuzsanna Lorántffy, but also the Catholic
prince, István Báthory . the entire Transylvania , the beginning to the present day, including the outstanding era of the principality, it deserves more than that. We cannot throw out of the window the colleges, printing houses,
churches, and even entire cities and castles and These are the places where the teachers and craftsmen
of the time, the princes who never denied their Hungarianness, saved and enriched the Hungarian language and Hungarian culture even at the cost of their lives don't want to generate a debate with this topic , the whole series, including this 44th episode, tries to bring the reader a summary of the facts. However, based on the work of historians, it should be known that as we move towards the year
2026 , the multifaceted , often contradictory approach to the evaluation of Mohács will become more and more common
One may ask how the Gyulafehérvár Cathedral, which is so often referred to as a - the easternmost Romanesque church in Europe and where the tomb of the Hunyadis is located - still
includes the tomb of the great reformed sons of Transylvania.
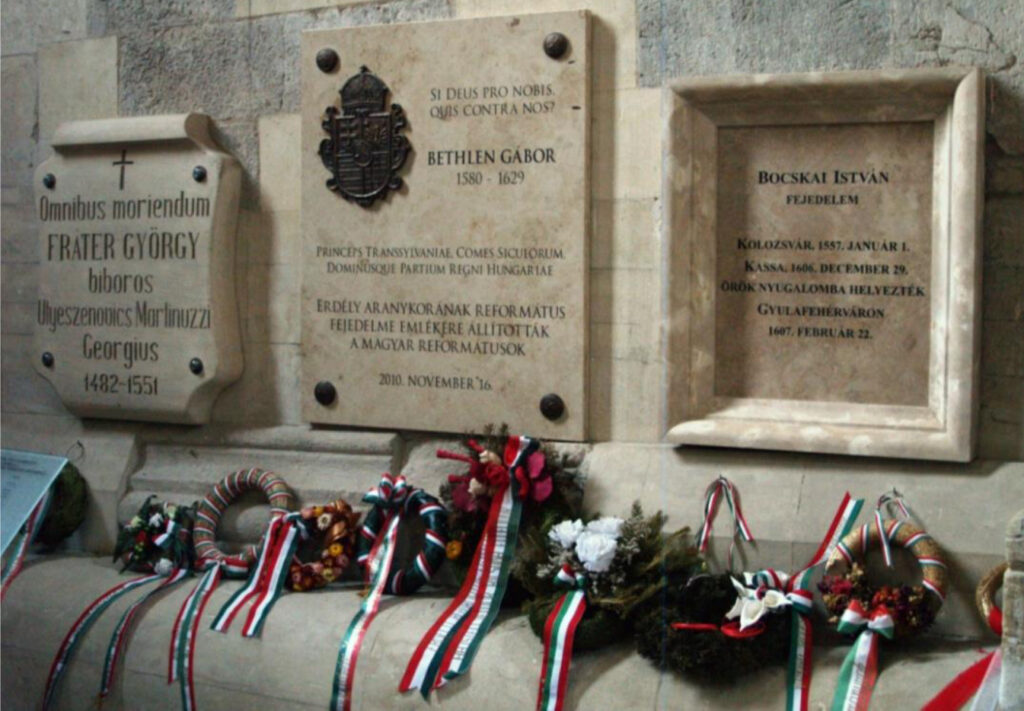

In the Gyulafehérvár Cathedral, next to the Catholic Fráter György, in a worthy place, near the sarcophagus of the Hunyadians, the two great figures of the Reformation, István Bocskai and Gábor Bethlen, sleep their eternal sleep.
What could have been the reason why the four Rákóczi princes - I. and II. Rákóczi , and I. and II. Ferenc Rákóczi - the great-grandfather and grandfather Reformed , and the grandson and great-grandson Roman Catholic? The short answer is that the
fate of the country and their lives depended on them changing their religion. II. György Rákóczi's wife, the tough old lady of the Catholic Báthory family, was able to save the life of her son (Ferenc I. Rákóci), who was involved in the lord's conspiracy, when a Catholic .
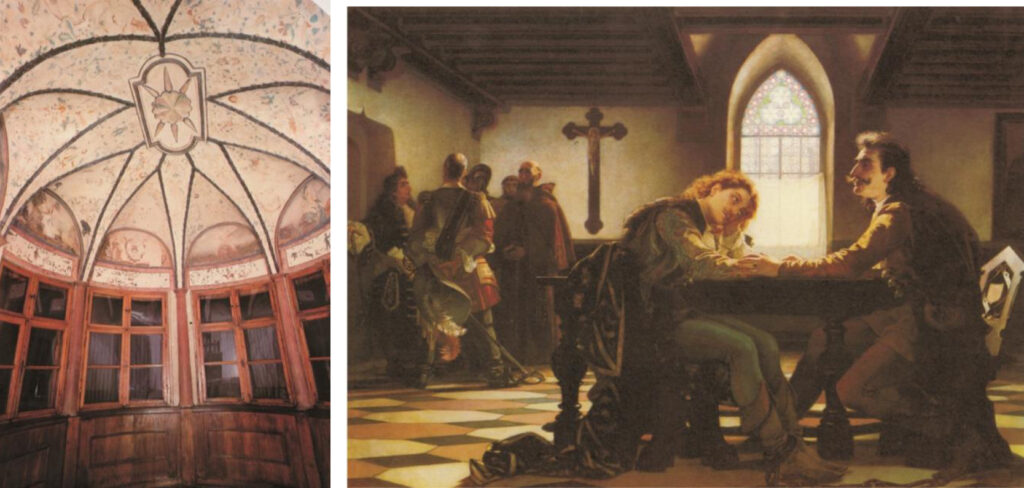

The location of the lord's conspiracy is the Sub Rosa room at Sárospatak Zrínyi and Frangepá in the prison in Bécsujhely (Viktor Madarász).
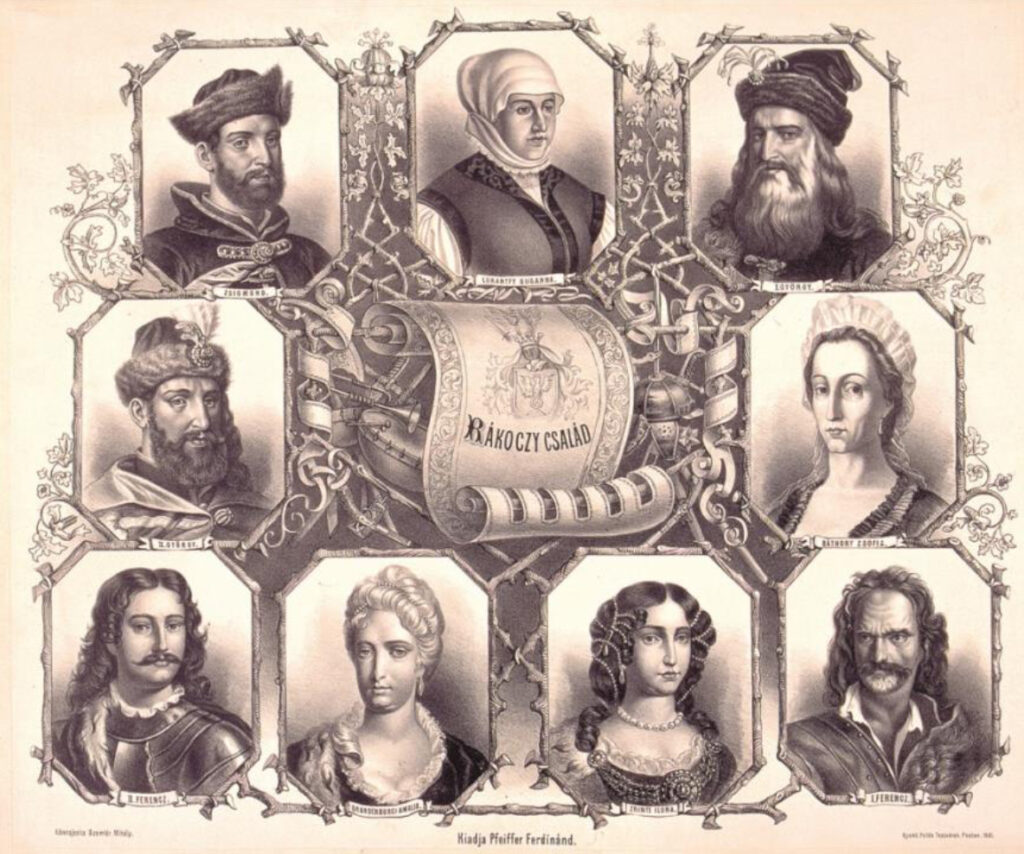

Among the wives in the Reformed Rákóczi family, only Zsuzsanna Lorántffy was a Reformed woman, the others were Catholics
The meeting of the Rákócs and the Zrínys is particularly interesting and characteristic of the diversity, religious and geographical affiliation of Hungarian history The Rákócs eastern region of the country and Transylvania , practicing both the Reformed and Catholic
faiths . The people of Zrín lived in the south-western region of the country, tied to Vienna, as half- Croatians, half-Hungarians on their huge estates. Prominent politicians from both families wanted the same thing as the other Hungarian lords who played a role in politics,
the unification of the country. Zrínyi before the Viennese wild boar . That is why Ferenc Rákóczi and his mother, Ilona Zrínyi, had to go into exile That is why Bocskai had to die prematurely and the evangelical Imre Thököly had to flee his country. We can see where religion unites and where it separates. Who was the "better Hungarian"? The Reformed or the Catholic? It always depended on how he was connected to his religion, and at least as important , how he was connected to his country.
Because Péter Pázmány was a great man, an important statesman, in addition to his outstanding ecclesiastical role. Lipót Kollonich who followed him later ? The Hungarian archbishop of Esztergom, with
Austrian - the values of his predecessor. Ped was not without talent, it is just his attitude that shows his place in Hungarian history. is expressed in a quote from him "I will make Hungary a prisoner, a beggar, and finally a Catholic!" When
little Rákóczi was separated from his mother, he was placed under the guardianship of Kollonich, who tried to "re-educate" the child in Czech and Austrian schools. It failed, as the historical example proved.
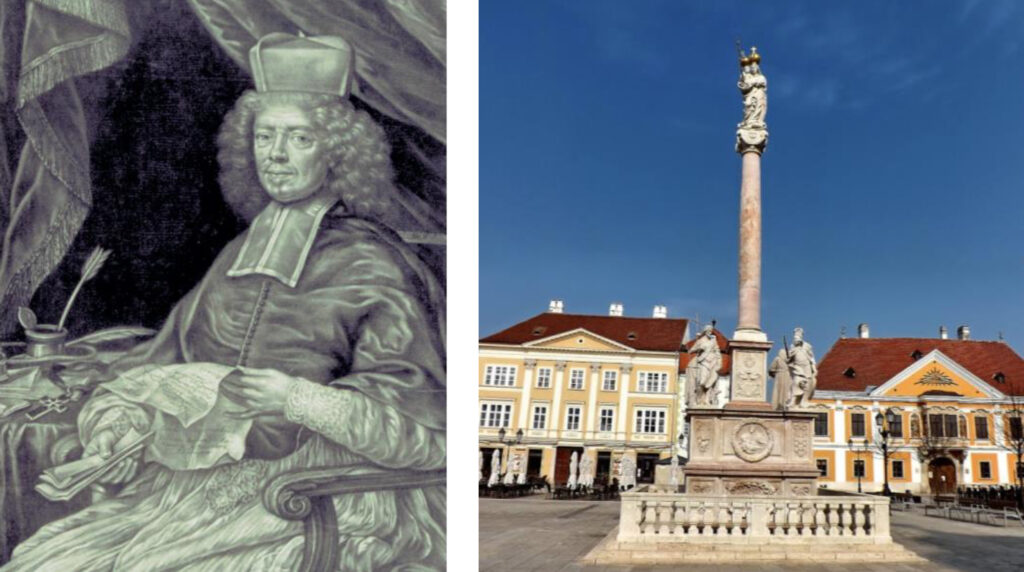

Lipót Kollonich, the rosy-minded Archbishop of Esztergom. The column of Mary in downtown Győr, erected by Archbishop Kollonich - formerly the bishop of Győr - in 1686, on the day of the recapture of Buda
Hungary and Transylvania, religion no longer has such a decisive role as, for example, it did in the 16th and 17th centuries. However, we acknowledge with satisfaction that it still larger than to the west of us, where so much blood flowed between the Catholics and the Reformed. Maybe even then just for power and money.
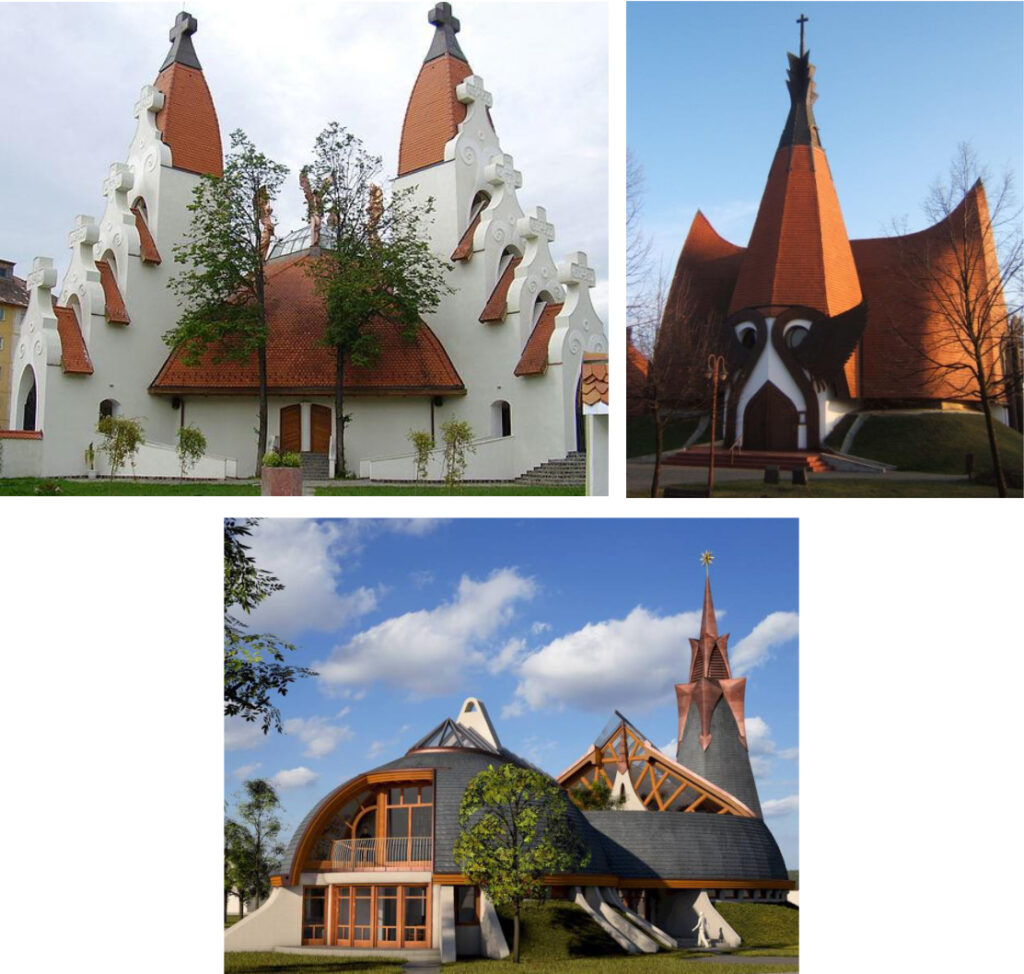

In Hungary and Transylvania in the 21st century, Roman Catholic churches and Reformed monuments are being built one after the other. The Roman Catholic Angelic Church in Csíkszereda, the Lutheran Church in Siófok, and the Reformed Church in Pesterzsébet are three examples of dozens of Makovecz buildings. The selected church buildings confirm the ecumenical worldview of one of the greatest figures of Hungarian architectural art and a Hungarian thinker
The wheel of history is turning! Who knows, seeing the state of Europe today, should we discard any of established religions? Be it Roman Catholic , Lutheran, Greek Catholic or Reformed, to mention only the most populous churches
. However, the common feature of the listed Christian religions is that they had and still have individuals who during the centuries of Hungarian history Let's think about this when we criticize any religion ,
or when anyone elevates his church above the others in addition to his religious commitment.
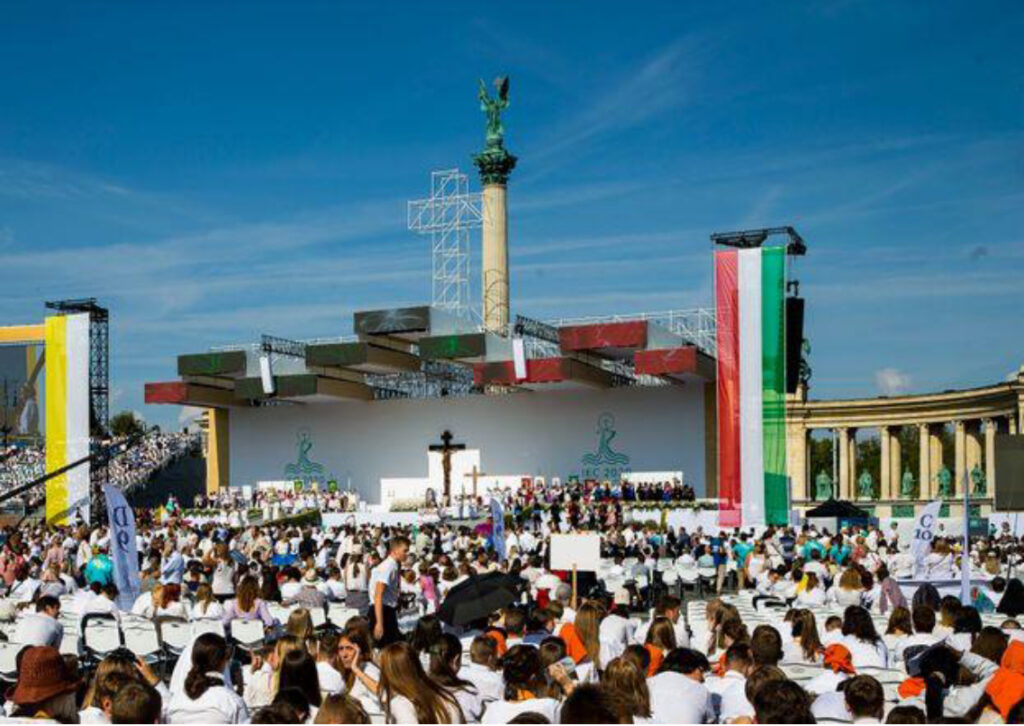

The 52nd International Eucharistic Congress September 5-12, 2021. took place in Budapest between The central event was held in Hősök Square. The significance of the event cannot be expressed only in the fact that Hungary hosted the world congress. We can also see that since Pope Francis' visit to Hungary, there has been a noticeable "change" in his speeches regarding the acceptance of Hungarian issues - family policy, the migrant crisis, the defense of Christianity
( We continue)
Ferenc Bánhegyi
The parts published so far can be read here: 1., 2., 3., 4., 5., 6., 7., 8., 9., 10., 11., 12., 13., 14., 15., 16., 17., 18., 19., 20.,21.,22., 23.,24,, 25.,26., 27.,28.,29/1.,29/2., 30., 31., 32.,33., 34.,35., 36.,37.,38., 39., 40., 41., 42. 43,












